Wind Turbines
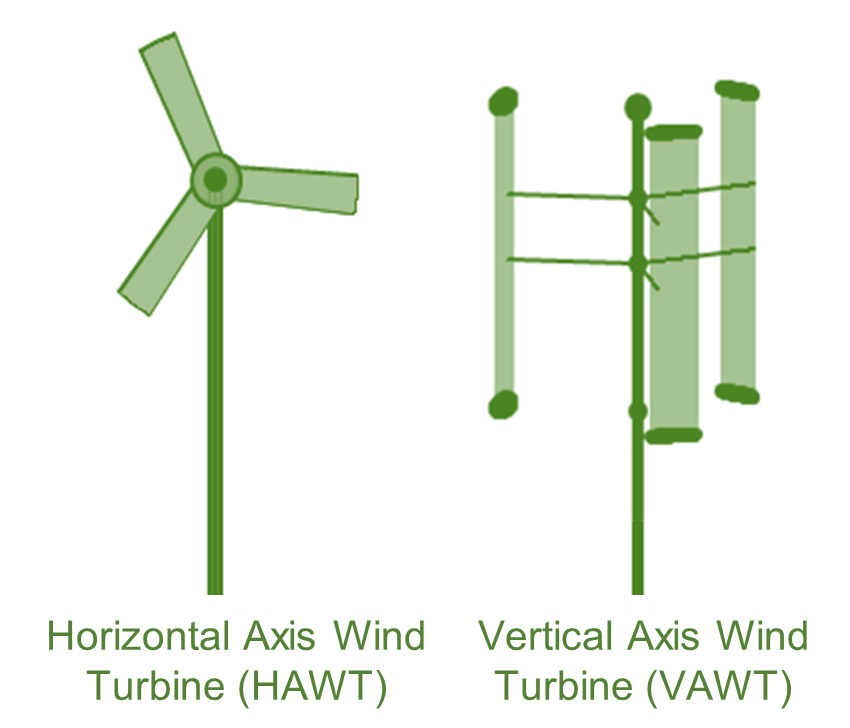
A wind turbine is a device that converts the wind’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. Wind turbines can rotate about either a horizontal or a vertical axis.
The advantage of wind over solar is that wind occurrence is not restricted to daylight hours.
The disadvantage of wind is its low predictability, geographic restrictions and potential planning approval requirements. There are steps that can be taken to overcome the disadvantages, these include site wind resource assessments and wind turbine selection.
Wind turbines are available in two types:
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT)
- Main rotor shaft runs horizontally
- More productive, more common
- Require moderate wind speed constantly
- High maintenance requirement
- High operational noise
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT)
- Main rotor shaft runs vertically
- Less productive, less common
- Can operate at low wind speed, in turbulent flow
- Cheaper, easier installation and maintenance
- Imperceptible noise
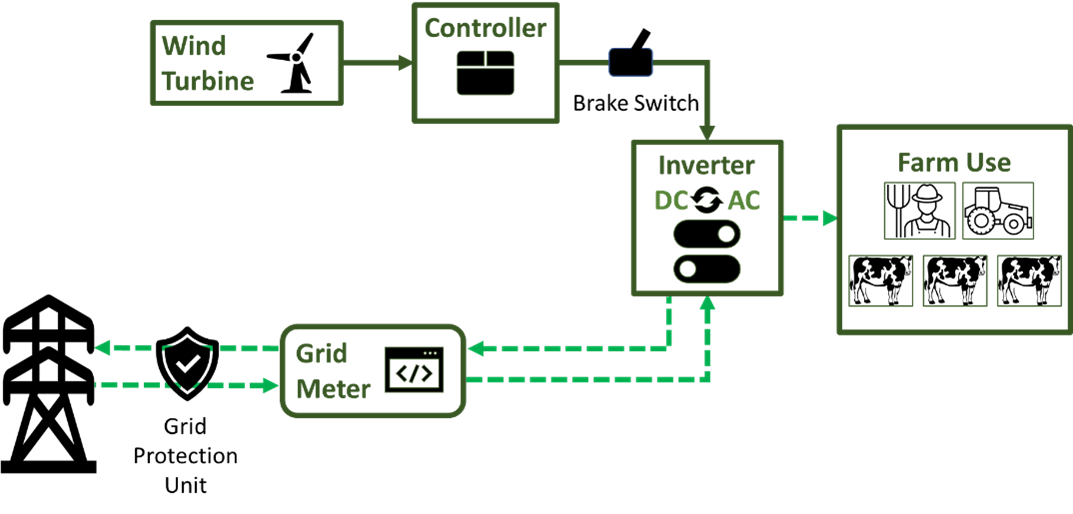
Ellinbank Configuration
Key Components
- Wind turbine and tower: assessed and installed at appropriate location and height to generate energy and ensure safety.
- Controller: continuously monitors the condition of the wind turbine and collect statistics on operation. It features with a dump load to prevent the system from freewheeling and overheating.
- Inverter: converts the variable direct current (DC) output from wind turbines into 240V 50Hz alternating current (AC). This AC electricity is used for farm applications.
- Grid-tied system: can purchase electricity from the grid when wind insufficient. Excess electricity can be sold back to the electricity grid.
- Brake switch: when the brake is released, the turbine spins naturally. Switching on the brake automatically or manually, ensures the turbine stops when detecting strong wind or any defects.
Learnings
- Every site can vary significantly, requiring an assessment of the location, energy requirements, integration and expandability, system design, operating conditions and of course, budget.
Consider design options such as horizontal or vertical axis to suit the farm demands and conditions. - To determine whether a wind turbine will generate enough energy at a site, a wind resource assessment should be conducted.
- Although it takes time, a site’s wind resource can be tested by temporarily installing an anemometer at the design height and location of a proposed wind turbine. The anemometer will track and log the wind resource, including time-stamped parameters such as wind velocity and direction.
- Do you consider on-grid or off-grid mode, or a combination? Do you have a generator on site, and do you want to integrate it into the system?
- Each system has a maximum wind speed at which the brake should be applied (or if automatic, comes into operation). The brake system is critical to protect the system. The farm management team require training from the supplier on when and how to operate a manual brake switch. Otherwise seek products with an automated brake solution and ensure there is power backup to make it work during extreme weather and power blackouts.
- Weather monitoring is recommended. A weather station may be required to allow monitoring of wind conditions and the turbine’s energy performance.
- Research your preferred suppliers. Ask previous clients about them, ask for references. Get at least two quotes to compare. Lock in a contract that lists all costs, timelines, warranty and defects liability period.
- Have a budget in mind. Note that items such as platforms, fences, metering and monitoring are likely to cost extra.
- Find out about the expected life of the equipment, likely returns and payback. Consider potential maintenance and interest costs.
- Get an inspection and certification. Check with local council if a permit is required or exempt before purchase.
Ellinbank SmartFarm Wind Turbine System
Further Information
The Ellinbank SmartFarm in Gippsland is Australia’s leading dairy innovation facility, fast-tracking innovative technology solutions in a research environment and showcasing them to the dairy industry. The Ellinbank SmartFarm has a target of becoming a carbon-neutral dairy farm and generating electricity through a range of alternative energy generation options including solar, wind and hydro energy will help achieve this goal.
See the Ellinbank Dashboard for more details.
Download: Ellinbank – Fact Sheet – Wind Turbine (PDF – 654KB)