Soil-borne diseases can be very damaging to field crop production. In extreme cases they can cause losses greater than 50 per cent, but often, due to their subterranean nature, losses go unrecognised. This lack of awareness and a lack of in-crop control options does make management of soil-borne diseases difficult.
Fortunately, DNA based soil testing (PREDICTA® B) provides the ability to identify paddocks at risk of damage from soil-borne diseases prior to planting, enabling appropriate management to be implemented to minimise losses.
This chapter provides an overview of the identification and control of some of the important soil borne diseases to Victorian field crops.
Soil borne disease distribution
The pathogens of soil-borne diseases are widespread within Victorian cropping soils. In Victoria the most common soil-borne pathogens of cereal crops are root lesion nematodes (RLN), crown rot, Rhizoctonia root rot, take-all and cereal cyst nematode (CCN). Within pulse crops soil-borne diseases are not very well understood, but both Phytophthora root rot and stem nematode are found in isolated cases.
Even though soil-borne diseases are common, their level within a given paddock will vary depending on the region and the paddock’s cropping history and weed control. Because of this it is best to not generalise about pathogen distribution and monitor each paddock for the soil-borne diseases present.
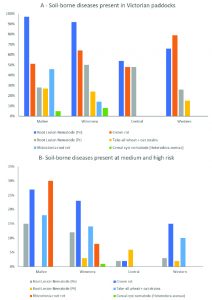
Cereal soil-borne diseases in Victorian paddocks based on 759 PREDICTA®B test results (2014-2017): A) percentage of paddocks where pathogens were detected, and B) percentage of paddocks where pathogens were detected in either the medium or high risk category.
Soil-borne Disease Identification
Effective management of soil-borne diseases begins with the accurate identification of pathogens in the paddock through either a soil test or inspection of plant roots for disease symptoms.
Soil Test
The PREDICTA®B soil test is the most accurate and comprehensive way of monitoring soil-borne pathogens in paddocks. This test can be used before sowing to identify paddocks at risk of soil-borne diseases, thus allowing high risk paddocks to be planted to another variety/crop to reduce the impact of soil-borne pathogens. The test can also be used in-crop to assist with disease diagnosis. When taking a soil test, it is important to correctly follow sampling protocols.
Inspection of Roots
To identify soil-borne diseases during the growing season, suspect plants can be dug up and their roots inspected. Plants should be sampled using a spade and not pulled out of the ground. This will ensure a good sample of roots is available for inspection. Soil is then carefully washed from the roots under running water. Roots are best inspected for disease by floating them in a white tray of water and looking for the different disease symptoms as described in this chapter.


